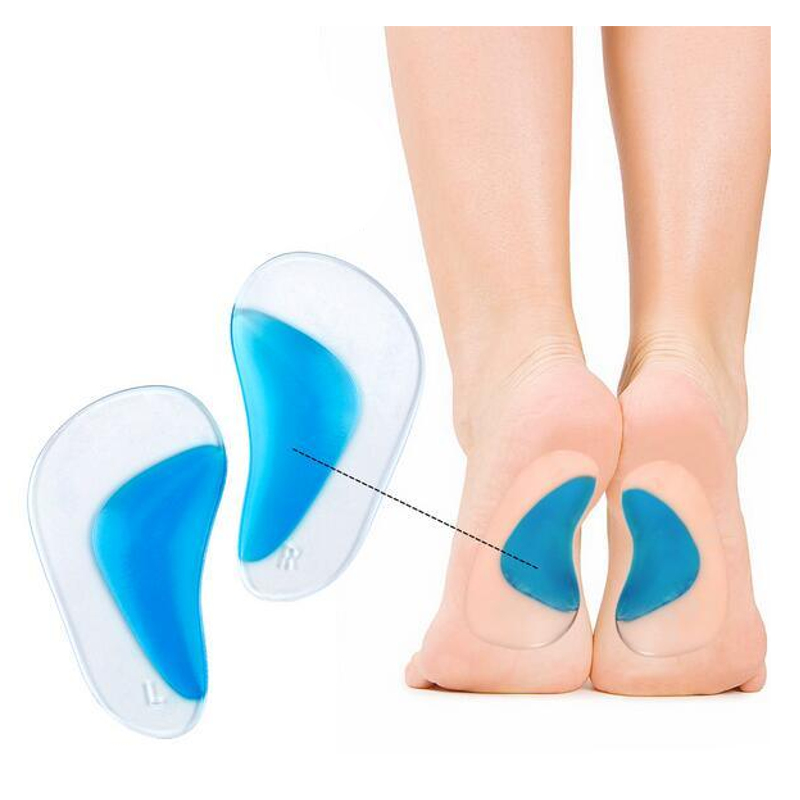
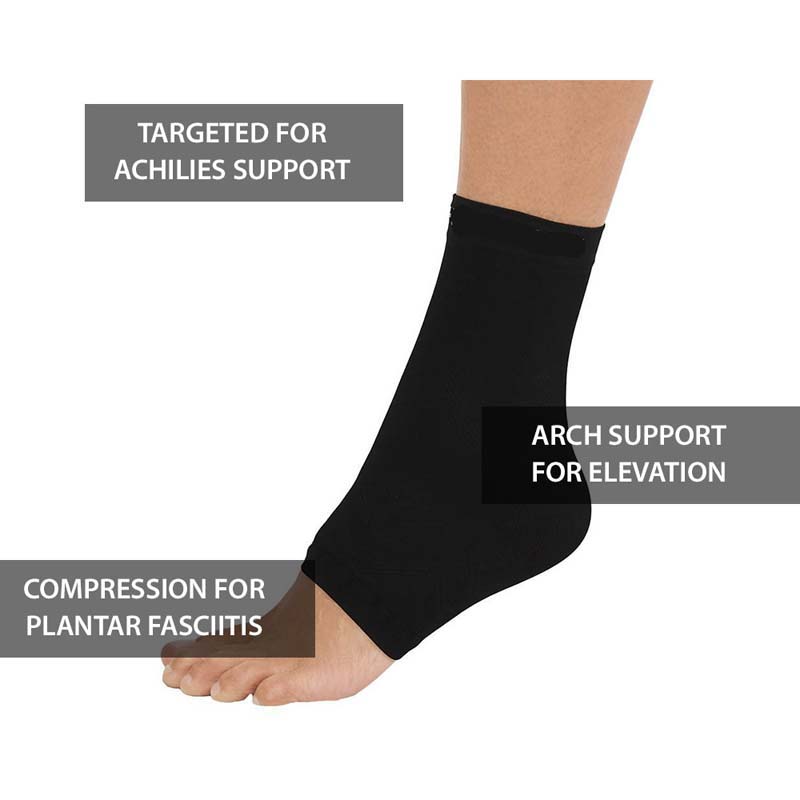
Heel Pain 101: A Guide to Plantar Fasciitis

Featured Products for Plantar Fasciitis Foot Pain Relief
Heel pain can be a persistent and debilitating condition, and one of the most common culprits is plantar fasciitis. This inflammatory condition of the plantar fascia—a thick band of tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot—can cause discomfort and impact daily activities. In this comprehensive guide, well delve into the key aspects of plantar fasciitis, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and effective management strategies.
Understanding Plantar Fasciitis:
-
Causes:
- Plantar fasciitis is often caused by repetitive stress on the plantar fascia, leading to small tears and inflammation. Common factors include excessive walking, running, or standing, as well as wearing shoes with inadequate support.
-
Symptoms:
- The hallmark symptom is heel pain, typically felt on the bottom of the foot near the heel. Pain is often most pronounced during the first steps in the morning or after periods of rest. It may improve with activity but return after prolonged standing or vigorous exercise.
Diagnosis:
-
Medical Evaluation:
- A healthcare professional, such as a podiatrist, will conduct a thorough examination, including a discussion of symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle factors.
-
Physical Examination:
- The healthcare provider may perform physical tests, such as the "windlass test" to assess pain during dorsiflexion of the toes, and evaluate gait and foot mechanics.
-
Imaging Tests:
- In some cases, imaging tests like X-rays or ultrasound may be ordered to rule out other causes of heel pain or to assess the severity of the condition.
Effective Management Strategies:
-
Rest and Activity Modification:
- Give the affected foot adequate rest, avoiding high-impact activities. Modify activities that exacerbate symptoms.
-
Stretching Exercises:
- Incorporate gentle stretching exercises for the calf muscles and the plantar fascia. Regular stretching can improve flexibility and reduce strain.
-
Footwear Considerations:
- Wear supportive shoes with proper arch support. Avoid shoes with worn-out soles or inadequate support.
-
Orthotic Inserts:
- Consider using over-the-counter or custom-made orthotic inserts to provide additional support and alleviate pressure on the plantar fascia.
-
Ice Application:
- Apply ice to the affected heel for 10-15 minutes to reduce inflammation. Use a cloth or towel to protect the skin.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Medications:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen may be recommended to manage pain and inflammation. Consult with a healthcare professional before use.
-
Physical Therapy:
- A physical therapist can provide targeted exercises to strengthen the muscles of the foot and lower leg, improve gait, and address biomechanical issues.
-
Night Splints:
- Night splints can be worn to keep the foot in a dorsiflexed position while sleeping, preventing the plantar fascia from tightening overnight.
-
Corticosteroid Injections:
- In severe cases, corticosteroid injections may be considered to reduce inflammation and provide short-term relief. This is typically reserved for cases that do not respond to conservative measures.
-
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT):
- ESWT is a non-invasive procedure that uses shock waves to stimulate healing in the affected area. It may be considered for persistent cases.
-
Surgical Intervention:
- Surgery is rarely necessary and is considered only when conservative treatments have failed. Procedures may involve releasing the tension on the plantar fascia or removing damaged tissue.
Preventive Measures:
-
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Excess weight places additional stress on the feet. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of developing or exacerbating plantar fasciitis.
-
Proper Foot Care:
- Pay attention to foot hygiene, wear appropriate footwear, and address any foot issues promptly to prevent additional strain on the plantar fascia.
-
Gradual Exercise Progression:
- If starting a new exercise routine, progress gradually to avoid overloading the feet. Include proper warm-up and stretching.
Conclusion:
Plantar fasciitis, though challenging, is a manageable condition with the right approach. By understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms, seeking timely medical evaluation, and adopting a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals can effectively navigate heel pain and work towards optimal foot health.
Featured Products for Plantar Fasciitis Foot Pain Relief
Latest Blogs
- Taking a Stand Against Heel Pain: Practical Solutions
- Happy Heels, Happy Life: Banishing Foot Pain for Good
- The Road to Relief: Strategies for Combating Heel Pain
- Heel to Toe Wellness: Tackling Foot Pain Head-On
- Foot Pain Decoded: Understanding the Signals Your Feet Send
- Soothing Steps: Natural Remedies for Heel and Foot Pain
- Putting Your Best Foot Forward: Managing Heel Discomfort
- The ABCs of Happy Feet: Beating Heel and Foot Pain
- From Heel to Toe: Navigating Common Foot Pain Issues
- Taking a Step Back: Causes and Remedies for Heel Pain
- Footloose and Pain-Free: Tips for Happy Heels and Feet
- Soleful Solutions: A Guide to Alleviating Heel and Foot Discomfort
- Stepping Into Comfort: Understanding Heel and Foot Pain
- From Pain to Progress: Inspiring Plantar Fasciitis Journeys
- Living a Full Life with Plantar Fasciitis: Success Stories
- Plantar Fasciitis and Exercise: Finding the Right Balance
- The Impact of Stress on Plantar Fasciitis Symptoms
- Plantar Fasciitis: When to Seek Professional Help
- Inflammatory Foods and Plantar Fasciitis: What to Avoid
- Ergonomics and Plantar Fasciitis: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Importance of Rest in Plantar Fasciitis Recovery
- Traveling with Plantar Fasciitis: Tips for Happy Feet
- Plantar Fasciitis and Your Sleep: Improving Rest Quality
- The Psychological Aspect of Living with Plantar Fasciitis
- Plantar Fasciitis and High-Impact Activities: Navigating Risks
- How to Stay Active with Plantar Fasciitis: Practical Tips
- Plantar Fasciitis and Aging: Strategies for Seniors
- Cryotherapy for Plantar Fasciitis: Icy Relief for Your Feet
- Aquatic Exercise for Plantar Fasciitis: Dive into Healing
- Mindfulness and Meditation for Plantar Fasciitis Relief
- Heel Pain 101: A Guide to Plantar Fasciitis
- Finding Relief - Plantar Fasciitis Home Remedies
- The Emotional Toll of Chronic Plantar Fasciitis
- Post-Workout Foot Care for Plantar Fasciitis Sufferers
- DIY Foot Massage Techniques for Plantar Fasciitis
- From Diagnosis to Recoveryc- Navigating Plantar Fasciitis
- Plantar Fasciitis in Children Signs and Solutions
- Plantar Fasciitis and Weight: Impact on Foot Health
- How Nutrition Affects Plantar Fasciitis Recovery
- Yoga for Plantar Fasciitis: Poses for Pain Relief
- Breaking Down Plantar Fasciitis Myths and Misconceptions
- Plantar Fasciitis Stretches - Daily Routine for Relief
- The Link Between Plantar Fasciitis and Flat Feet
- Plantar Fasciitis in Pregnancy - What to Expect
- Desk Job Dilemma - Coping with Plantar Fasciitis at Work
- Plantar Fasciitis in Athletes Strategies for Recovery
- Massage and Plantar Fasciitis A Soothing Combination
- Plantar Fasciitis at Night: Tips for Better Sleep
- Plantar Fasciitis vs Heel Spurs - Understanding the Difference
- The Role of Stretching in Plantar Fasciitis Recovery
- Running with Plantar Fasciitis: Dos and Donts
- Preventing Plantar Fasciitis: Tips for Foot Health
- Natural Remedies for Plantar Fasciitis You Havent Tried
- Heel Pain Demystified: Plantar Fasciitis Explained
- Best Shoes for Plantar Fasciitis: A Comprehensive Guide
- Managing Plantar Fasciitis Pain: Tips and Tricks
- The Complete Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Treatment Options
- 10 Effective Exercises for Plantar Fasciitis Relief at Home
- Understanding Plantar Fasciitis: Causes and Symptoms
- Why do I get Pain in My Feet at Night
- Is pain in your feet a sign of diabetes
- What causes pain in my feet
- Plantar Fasciitis - Why so Painful
- What is that pain in my heel
- Should I Walk with Foot Pain
- How to Treat Ankle Pain
- 10 Best Exercises of Plantar Fasciitis
- Do Compression Socks Help Foot Pain
- Do Insoles Work for Foot Pain
- Best Stretches for Plantar Fasciitis
- 5 Causes of Plantar Fasciitis
- Do Back Posture Braces Actually Work
- Foot pain from walking
- Best Insoles for Plantar Fasciitis
- Pain in heel of foot after Running
- Treatment for Pain in arch of foot
- Pain on top of foot
- Mortons neuroma treatment
- How to remove an Ingrown Toenail
- Foot Heel Spur Pain
- Sore Foot in the Morning
- Suffer Heel Pain in the Morning ?
- Start a running routine
- Running through Fatigue
- Best Achilles Tendonitis and Ankle Excercises
- Causes of Achilles Tendonitis and Ankle Pain
- Plantar Fasciitis Cure and Treatment
- Best Plantar Fasciitis Products
- Causes of Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Spur Pain
- Best Plantar Fasciitis Excercises